The constellation Orion, named after a prominent hunter in Greek mythology, is one of the most recognizable and prominent constellations in the night sky. The constellation offers a breath-taking view of several celestial wonders, including its prominent Belt of three stars and various nebulae. Here are some key details about the constellation Orion:
Location
Orion is located on the celestial equator and can be seen from both the northern and southern hemispheres. It is situated along the celestial equator, making it visible to observers in a wide range of latitudes. Its positional coordinates in the sky are described by the range of right ascension (RA) and declination (Dec) values that encompass the constellation.
Right Ascension (RA): Approximately 4h 30m to 6h 20m
Declination (Dec): Approximately -10° to +20°
Positional coordinates are a system used by astronomers to locate objects in the sky. They are based on the celestial sphere, an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth where all celestial objects appear to reside. Two primary coordinates are used:
Right Ascension (RA): Similar to longitude on Earth, RA measures an object’s east-west position in the sky, expressed in hours, minutes, and seconds. It starts from the vernal equinox (0h RA).
Declination (Dec): Similar to latitude, Dec measures an object’s north-south position relative to the celestial equator, expressed in degrees (°), arcminutes (‘), and arcseconds (“).
These coordinates help astronomers precisely pinpoint celestial objects and align telescopes for observation.
Shape and Stars
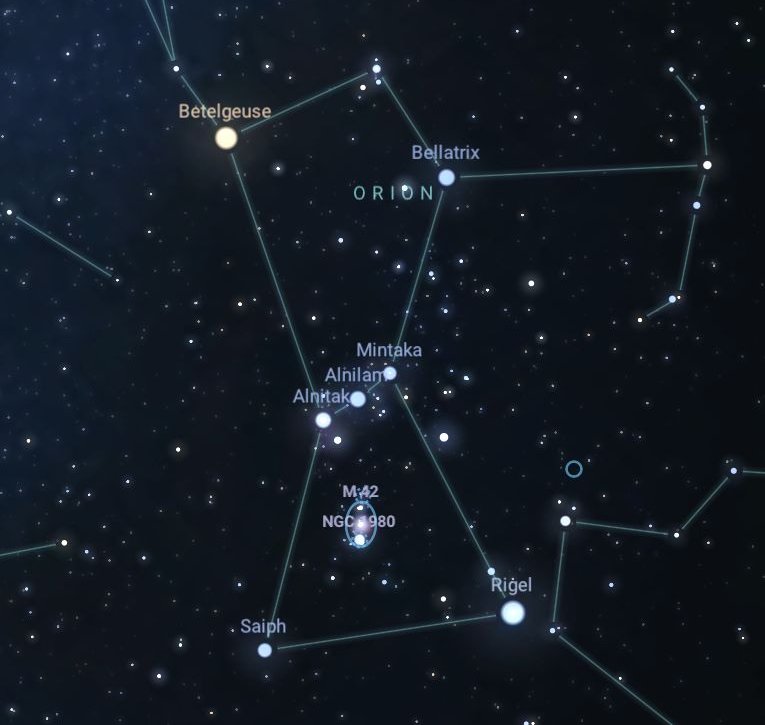
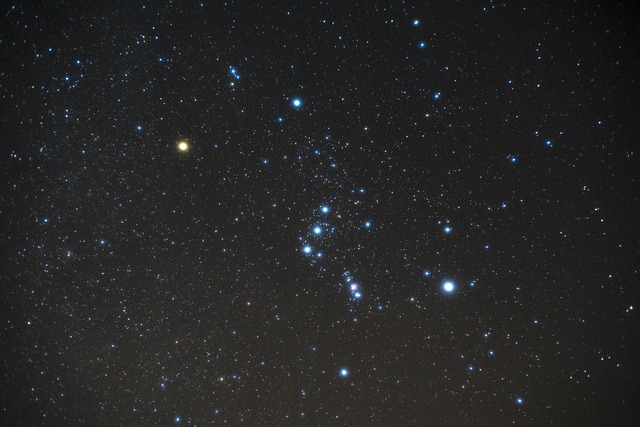
Orion is known for its distinctive shape, which is often likened to that of a hunter. It contains several bright stars that form the outline of the hunter’s body, including Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) and Rigel (Beta Orionis), which are two of the brightest stars in the night sky. Orion’s Belt, consisting of three bright stars named Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka, is another prominent feature of the constellation.
The stars in Orion range from about 240 light-years (Bellatrix) to over 2,000 light-years (Alnilam) from Earth. These distances highlight the diversity of Orion’s stellar members, which together form one of the most iconic constellations in the night sky.
Mythology
In Greek mythology, Orion was a giant and a skilled hunter. According to legend, he was eventually killed by a scorpion sent by the goddess Artemis, who was jealous of his prowess. To honour Orion, the gods placed him among the stars as the constellation that bears his name.
Nebulae
The constellation Orion is also home to several notable nebulae, including the Orion Nebula (M42) and the Horsehead Nebula (Barnard 33). The Orion Nebula is one of the brightest and most easily visible nebulae in the night sky and is a region of active star formation.
Winter Constellation
Orion is a prominent constellation in the winter sky in the northern hemisphere (November–February), and the summer sky in the southern hemisphere (December–March). It is often used as a guide for locating other stars and constellations due to its distinctive shape and prominent stars.

Star Magnitudes
Here are the magnitudes of some of the most well-known stars in the constellation of Orion:
Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis): Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. Its apparent visual magnitude varies between about 0.0 and 1.3, making it one of the brightest stars in the constellation.
Rigel (Beta Orionis): Rigel is a blue supergiant star and the brightest star in the constellation of Orion. Its apparent visual magnitude is approximately 0.12, making it one of the brightest stars in the sky.
Bellatrix (Gamma Orionis): Bellatrix is a blue giant star and one of the brighter stars in Orion. Its apparent visual magnitude is about 1.64.
Alnilam (Epsilon Orionis): Alnilam is a blue supergiant star and one of the three stars that form Orion’s Belt. Its apparent visual magnitude is approximately 1.70.
Alnitak (Zeta Orionis): Alnitak is another star in Orion’s Belt. It is a triple star system, and its combined apparent visual magnitude is approximately 1.74.
Mintaka (Delta Orionis): Mintaka is the third star in Orion’s Belt. Its apparent visual magnitude is approximately 2.21.


