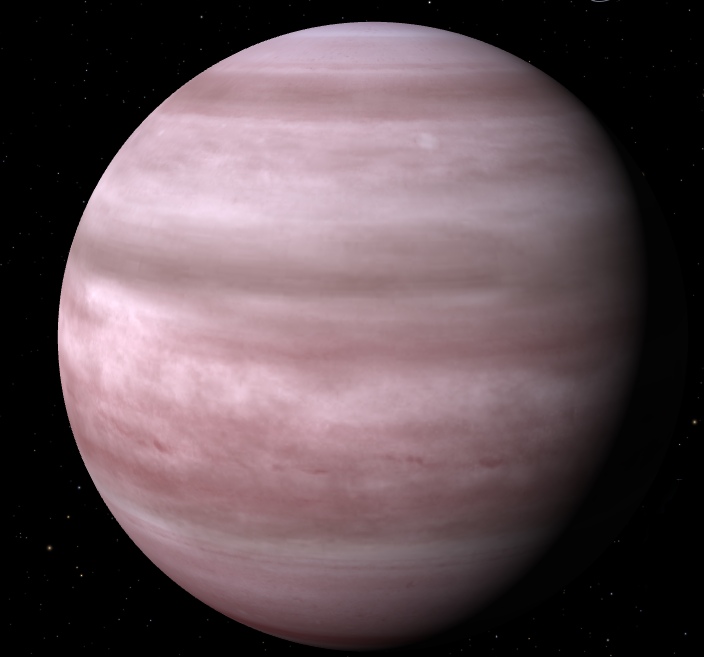
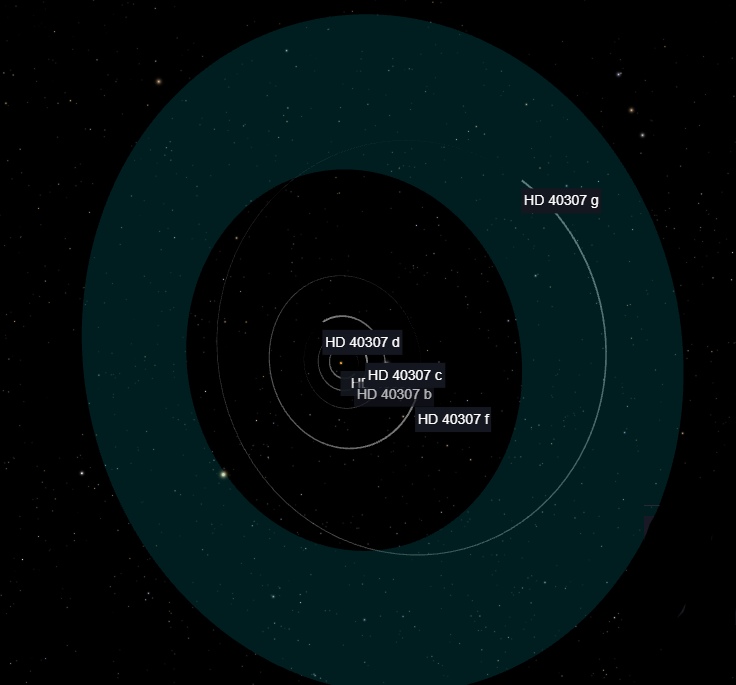
HD 40307g is one of six exoplanets located in the HD 40307 system, approximately 42 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Pictor. Here are some key points about HD 40307g:
Discovery
HD 40307g was discovered in 2012 by a team of astronomers led by Mikko Tuomi using data from the European Southern Observatory’s HARPS spectrograph. It was detected through the radial velocity method, which measures the slight wobble of a star caused by the gravitational pull of an orbiting planet.
Characteristics
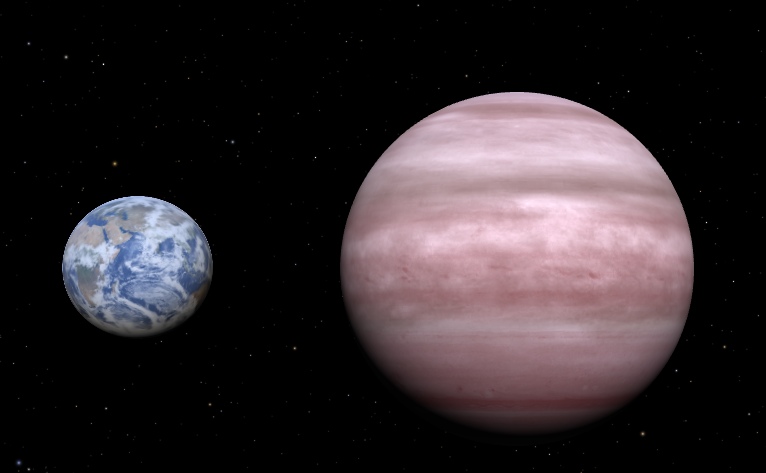
The exoplanet is classified as a super-Earth, with a mass estimated to be about 7 times that of Earth. It orbits its host star within the habitable zone, where conditions might be suitable for the existence of liquid water on its surface. Its orbital period is approximately 197.8 days.
The host star is a K-type dwarf star called HD 40307. K-type dwarfs are smaller and cooler than the Sun, and they are relatively common in the galaxy.
Habitability
The discovery of HD 40307g within the habitable zone raised speculation about its potential habitability. Its location, size, and estimated surface temperature suggested it could have conditions similar to Earth. However, the actual habitability of HD 40307g remains uncertain, and further observations are needed to determine its atmospheric composition and surface characteristics.
While there are no direct measurements of its atmosphere, scientists speculate that HD 40307g could have a thick atmosphere potentially rich in gases such as carbon dioxide or water vapor. Its size suggests that it might be capable of retaining a substantial atmosphere, which could create conditions for liquid water if the temperature and pressure are right. As for the surface, it is likely rocky, given its classification as a super-Earth. It could feature a diverse terrain, possibly with oceans or a landscape dominated by rocky or icy features, but without more detailed data, these characteristics remain speculative.
Follow-up Observations
Additional observations of the HD 40307 system, including HD 40307g, have been conducted using various telescopes and instruments to gather more information about the planet and its properties. These observations aim to refine our understanding of the system and its potential for hosting habitable planets.
Obsevation
Exoplanets are beyond the visibility range of amateur telescopes. However, the host star, HP 40307, is still visible in binoculars and telescopes.
HD 40307 is located in the constellation Pictor, which is best viewed from the Southern Hemisphere. The star is visible during the summer and early autumn months, specifically from December to March.