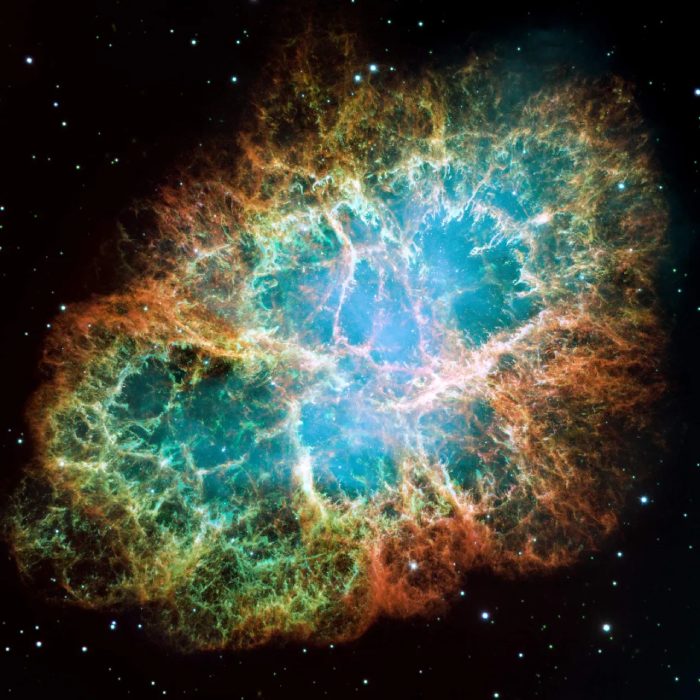
The Crab Nebula, also known as Messier 1 (M1), is one of the most famous and studied supernova remnants in the night sky. It is located in the northern constellation Taurus. Here are some key details about this celestial object:
Birth and Origin
M1 is the remnant of a supernova explosion that was observed and recorded by Chinese astronomers in 1054 AD. The progenitor star, which exploded in the supernova event, was a massive star several times more massive than the Sun. The explosion expelled its outer layers into space, creating the nebula we observe today.
It was later independently rediscovered by astronomers in the West in the 18th century and catalogued by Charles Messier as Messier 1 (M1) in his catalogue of non-cometary objects.
Appearance and Composition
The Crab Nebula appears as a diffuse, glowing cloud of gas with an irregular shape, marked by filamentary structures and wisps of material radiating outward from its core. It emits energy across the entire electromagnetic spectrum, from radio waves to X-rays.
Composed primarily of ionized gases such as hydrogen, helium, and other elements, the nebula also harbors a rapidly spinning neutron star at its center, known as the Crab Pulsar. This pulsar emits beams of radiation that sweep across space as it rotates, creating the nebula’s distinctive pulsating effect.

Size and Distance
The nebula is located approximately 6,500 light-years away from Earth and has a diameter of about 11 light-years. It is one of the closest supernova remnants to Earth, making it a valuable object for study by astronomers.
Observation
M1 is a popular target for amateur astronomers due to its brightness and historical significance. It can be observed with small telescopes and even binoculars under dark skies, although larger telescopes reveal more detail and structure within the nebula.
The Crab Nebula can be observed throughout the year since it is not tied to any specific season. However, its visibility depends on its position relative to the observer’s location and the time of night.
In general, the best time to observe the nebula is during the late autumn and winter months in the Northern Hemisphere (November to February) and during the spring and summer months in the Southern Hemisphere (December and January). During these times, the constellation Taurus, where the Crab Nebula is located, is well-placed in the sky during the evening hours, and the constellation reaches its highest point in the sky around midnight.